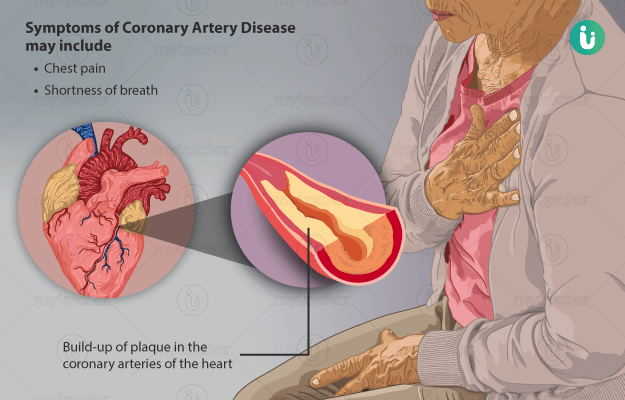
The first symptoms of coronary artery disease are a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest. A doctor can diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD) by screening a person for signs of atherosclerosis (a condition characterized by plaque buildup in the arteries). The symptoms of CAD are called non-specific because they may be caused by other conditions. In some cases, they may even be unrelated to the heart. Diagnosing CAD involves eliminating other possible causes of these symptoms.
Angina, or chest pain, is another symptom of coronary artery disease. The condition occurs when a part of the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Angina may also cause pain in the neck, jaw, back, and arms. It can also cause shortness of breath. If left untreated, CAD can lead to heart failure and arrhythmias, which can lead to cardiac arrest. Although the symptoms of coronary artery disease can vary, they are indicative of the disease.
The most common symptom of coronary artery disease is chest pain. Angina is a pain in the chest that is caused by a blocked artery. Usually, the symptoms of angina are accompanied by shortness of breath. The symptoms of coronary artery disease can also be severe and can lead to heart failure and arrhythmias. As with any other heart condition, treatment is essential to prevent complications. The symptoms of CAD can be treated in the first instance.
As with any disease, CAD can affect both men and women. While a family history of heart disease increases a person’s risk, lifestyle and genetic factors can reduce this risk. Exercise, weight loss, and healthy diets can all help prevent coronary artery disease. While it is not possible to prevent the onset of coronary artery disease, lifestyle changes and medicines can significantly improve the risk of developing the condition. However, if you’re unsure, talk with your doctor.
A lack of calcium in the blood is the most common cause of CAD. This is the most common symptom of CAD. A person with a deficiency of nitric oxide (Nitric oxide), a lack of Vitamin D, or fibrinogen may be at risk for the disease. These factors can contribute to an increased risk of coronary artery disease. For these reasons, a weakened heart can be a risk factor for CAD.

People with CAD may experience chest pain and angina. Angina is a painful condition caused by the lack of sufficient oxygen-rich blood flowing to the heart. Angina may affect the arm, neck, jaw, and back, but it can also occur in the neck, chest or jaw. A patient with CAD is at risk for a heart attack and may not even be aware of it. If a person is unaware of these symptoms, they may be suffering from an undiagnosed CAD.
Symptoms of coronary heart disease include chest pain and angina, which occurs when part of the heart muscle does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. Some people may experience pain in their arms, neck, and jaw, but they rarely have any physical signs. Other symptoms of CAD include heart failure and arrhythmias. In addition to chest pain, patients with CAD should seek immediate medical attention. They should not delay treatment and visit the health site regularly www.healthbrandsshop.com if they have any risk factors for coronary heart disease.
If you have a medical condition associated with CAD, it is important to see your doctor immediately. If you have a history of CAD, it may be time to check with your doctor. Your doctor will perform a stress test that includes walking on a treadmill or riding an exercise bike and monitoring your heart rate. During a stress test, the patient’s heart will be stimulated to increase its rate.
Symptoms of coronary heart disease include angina pectoris, chest pain, and swelling in the heart. Often the pain occurs during physical activities such as exercising or walking. IHD can cause other health problems, including heart attacks, arrhythmias, and heart failure. People with CAD can also suffer from depression. There are other causes of chest pain, including diseases of the lungs or esophagus.
Leave a Reply